class g airspace visibility requirements
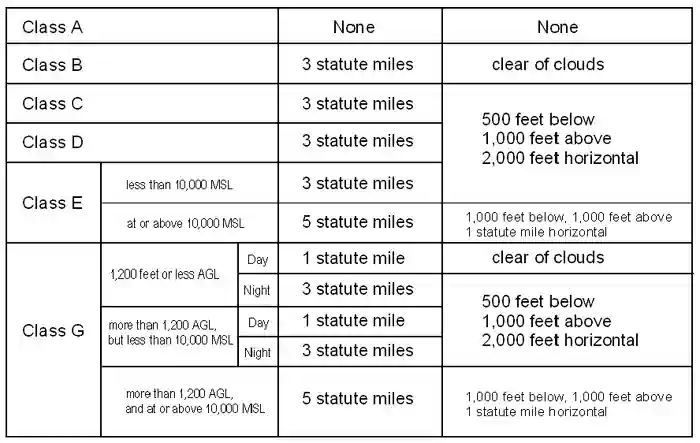
36 rows 2 If ground visibility is not reported at that airport unless flight visibility during. For example VFR flights are generally not allowed in Class A airspace so VFR visibility requirements do not exist for that class of airspace.
A helicopter may be operated clear of clouds in an airport traffic pattern within 12 mile of the runway or helipad of intended landing if the flight visibility is not less than 12 statute mile.

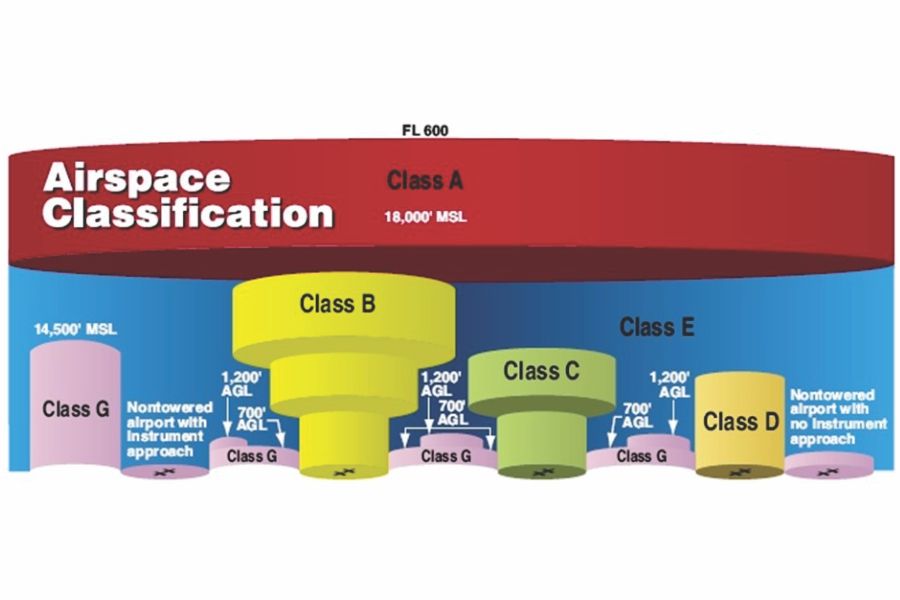
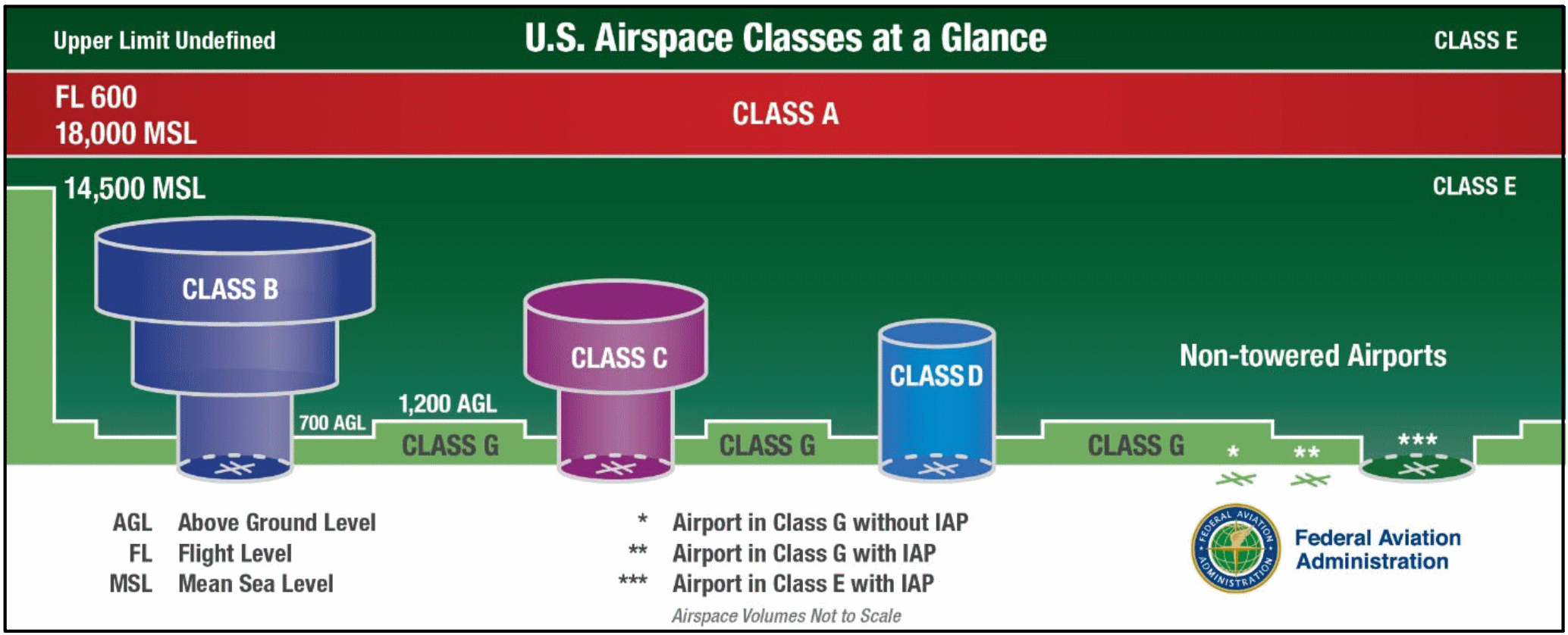
. At night requirements jump to three miles visibility and from merely clear of clouds to 500 feet below 2000 feet horizontal and. In summary Class G Airspace is the least restrictive of all airspaces. On the other hand Class G airspace has four different sets of altitude-dependent minimums.
Learn more about the eCFR its status and the editorial process. For example if Class E starts at 700 feet AGL Class G goes up to but doesnt include 700 feet AGL. VFR visibility requirements in class G airspace are 1 mile 16 km by day and 3 miles 5 km by night for altitudes below 10000 feet 3050 m MSL but above 1200 ft AGL.
Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft. Both class g vfr visibility requirements below 10000 ft msl and 1200 ft agl are 1 sm. Above the Class G ground is Class E everywhere else and is controlled airspace.
Although Class G is uncontrolled it is also subject to the most weather restrictions based on where the airspace is located. 18 rows Class D airspace is more restrictive than Class E or Class G airspace. In Class B airspace aircraft are required to remain.
The requirements are slightly less restrictive in Class G airspace with a less restrictive daytime visibility below 10000 feet MSL 1 statute mile only and below 1200 feet AGL by day a less-restrictive separation from clouds clear of clouds with no distance-from-cloud requirements. And Class E is. On a map Class Gs ceiling is the floor of Class E airspace.
A Unless otherwise specified in the certificate holders operations specifications when conducting VFR helicopter air ambulance operations in Class G airspace the weather minimums in the following table. A helicopter may be operated clear of clouds in an airport traffic pattern within 12 mile of the runway or helipad of intended landing if the flight visibility is not. Class g airspace weather visibility requirements.
Class G Airspace Weather Visibility Requirements. Class G airspace is most easily found on a sectional map when a fading thick blue line appears. Depending on how high you fly and the time of day within Class G airspace your visibility requirement could range anywhere from 1SM to 5SM.
This line shows enroute Class E airspace starting at. Class E and Class G airspace. However most regulations affecting pilots and aircraft still apply Pilots are reminded that in addition to IFR altitude or flight level requirements FAR 91177 includes the IFR requirement to remain at least 1000 2000 in mountainous.
Rules governing VFR flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft. Sport and recreational aviation activities. Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace.
All operations in Class A Class B Class C and Class D airspace or Class E airspace designated for an airport must receive prior ATC authorization as required in 10317 of this part. One mile visibility and clear of clouds is the daytime requirement. Except when associated with a temporary control tower ATC does not have responsibility for or authority over aircraft in Class G airspace.
1 mile visibility clear of clouds. Communications Airspace Features Class A Airspace Class B Airspace Class C Airspace Class D Airspace Class E Airspace Class G Airspace. And its always exclusive.
Class G Is The Most Lenient And Confusing. For Class B C D and E airspace below an altitude of 10000 MSL the basic VFR weather minimums are. Notwithstanding the provisions of paragraph a of this section the following operations may be conducted in Class G airspace below 1200 feet above the surface.
Above 1200ft stays at 1sm visibility but then for cloud clearance you must be 1000ft above 500ft below and 2000ft horizontal. 135609 VFR ceiling and visibility requirements for Class G airspace. Night minimums in Class G Airspace remain the same regardless of altitude.
Above that altitude Class G Airspace weather minimums increase to one statute mile visibility while remaining 500 feet below clouds 1000 feet above clouds and 2000 feet horizontally from clouds. The rationale for greater visibility and more distance from. Visibility or as much distance from clouds to see and avoid other traffic.
1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds. 1200ft or less above the surface regardless of MSL altitude Day. Class G airspace includes all airspace below 14500 feet 4400 m MSL not otherwise classified as controlled.
Airspace Requirements for Weather Minimums. You can remember Class G uncontrolled airspace because its just like the good old days at the dawn of aviation. Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds.
14 rows In all reality Class G airspace always ends well before 14500 msl due to another. No person may operate an ultralight vehicle when the flight visibility or distance from clouds is less than that in the table found below. Aircraft operating at higher altitudes ie Class E airspace above 10000 MSL are likely to be not only faster but also operating on instrument flight plans.
Cloud clearances range from clear of clouds to 1SM There are 6 sets of Class G weather minimums associated with various altitudes during the day or night. Air defence identification zone. Class G communications.

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

Airspace Classification Aspmhelp Aviation Education Flying Lessons Pilot Training

Airspace Classes Explained The Ultimate Guide For Beginners
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind

Uncontrolled And Controlled Airspace

Uncontrolled And Controlled Airspace

National Hurricane Services Legend Weather Map Map Symbols Aviation Education

This Is How Class G Airspace Works Boldmethod

Pin By S M K Kazimi On Flying Aviation Training Flight Training Flight Lessons
How To Remember Vfr Weather Minimums Bobbie Lind

Cruise Climb Rule Of Thumb Aviation Education Pilots Aviation Aviation Training

Sectional Chart Airspace Classification Overview Aerial Guide Chart Classification Cardinal Directions

Sectional Airspace Summary Pilotvintage Aviation Classes Student Pilot Flight Lessons

Vfr Cloud Clearances Pilot Training For Ga
Regulations Vfr Minimums Learn To Fly Blog Asa Aviation Supplies Academics Inc